 Men over the age of 50 are likely to face benign prostatic hyperplasia. Men with symptoms related to urination or storage are recommended to seek medical advice. (iStock image)
Men over the age of 50 are likely to face benign prostatic hyperplasia. Men with symptoms related to urination or storage are recommended to seek medical advice. (iStock image)
Lianhe Zaobao (29 May 2022)
Prostatic hyperplasia leads to varying degrees of urinary obstruction in men, and severe cases require treatment. What are the pros and cons of the treatment options?
Q I would like to speak with my doctor about the symptoms, diagnosis, and treatment options of an enlarged prostate. How do you know if you have benign prostatic hyperplasia? Besides traditional surgery, what other treatments can reduce side effects? Is there a designated suitable group for minimally invasive surgery? What are the pros and cons of the latest treatment options?
Answer BPH is a benign disease in which patients experience varying degrees of obstruction of urination due to the enlargement of the prostate gland at the outlet of the bladder. Symptoms of benign prostatic hyperplasia can be broadly divided into voiding symptoms and storage symptoms as follows:
benign prostatic hyperplasia symptoms
- Voiding symptoms: slow urine stream, intermittent urination, and tightness when urinating.
- Storage symptoms: frequent urination, nocturia, and sudden strong urge to urinate.
If you suspect that you have benign prostatic hyperplasia, you can ask your doctor for a diagnosis, including taking a personal medical history and doing a physical examination, such as a digital rectal exam (digital rectal exam) to examine the prostate, and blood and urine tests. Doctors will also discuss receiving a prostate-specific antigen (PSA) test and other auxiliary tests, such as uroflowmetry, which can be done in a specialist clinic. X-ray imaging or ultrasonography can detect the presence of urinary stones and assess the size and shape of the prostate. These tests help rule out other factors such as infection, stones, or cancer, and also help assess the severity of the disease. Generally, men over the age of 50 are likely to face benign prostatic hyperplasia, especially older men. In addition, men with any of the above symptoms related to urination or storage are also advised to see a doctor for diagnosis.
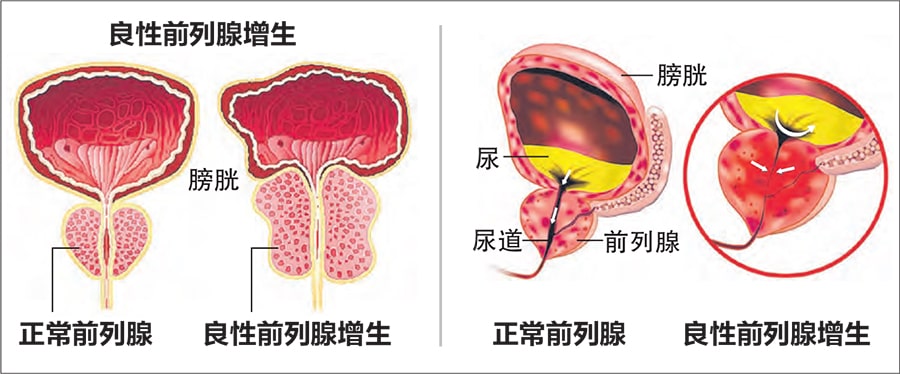 The difference between normal prostate and benign prostatic hyperplasia. (iStock image)
The difference between normal prostate and benign prostatic hyperplasia. (iStock image)
Choose treatment based on severity of symptoms
In addition to discussing lifestyle management, physicians also discuss medications, which are often one of the first-line treatments, with patients. Lifestyle recommendations are individual. People with nocturnal urination should reduce their nighttime fluid intake, avoid caffeinated beverages, and avoid regular alcohol or smoking habits that may aggravate symptoms.
患者可服用的药物种类繁多。这 通常属于永久的治疗方法,须每日服 用药物,直到完成其他治疗方法。药 物副作用可包括头晕和性功能障碍。
症状较严重或服用药物后症状没改善的患者,往往可选择接受手术治 疗。这类病患通常可在术后停止服用 药物。
MIST对比TURP
微创手术治疗( m i n i m a l l y invasive surgical treatments,简称 MIST)可包括使用Rezum水蒸气微 创疗法把细长仪器植入尿道,利用蒸 气在前列腺细胞间扩散时杀死多余细 胞,缩小前列腺,或是用Urolift系统 微创疗法,从尿道置入细长仪器,仪 器往两旁前列腺发射微型植入物,把 前列腺肿大的部位从尿道拉回且固 定,开通尿道。
选择接受MIST的患者,射精功 能的影响可降至最低,术后尿中有血 的情况也较少。然而,与常规手术如 经尿道前列腺切除术(TransUrethral Resection of the Prostate,简称 TURP)相比,MIST治疗后的尿流率 和症状的改善会稍差。
相较TURP和药物治疗,MIST也 属于较新的技术,在国际上已使用 约五到十年,本地泌尿科医生使用 MIST则约有四到五年。
一般上,症状较少的患者或前列 腺增生属轻度且阻塞情况轻微的人, 通过药物治疗或MIST便可改善。因 此,一般建议年纪较轻、性生活活 跃,以及症状较轻微且膀胱出口阻塞 程度较轻的患者接受MIST治疗。
另一方面,年纪较大、性生活不 活跃,症状较严重或前列腺增生显 著,而且膀胱出口阻塞程度较严重的 人,若是对药物治疗效果不大时,接 受常规手术治疗的效益往往较大。
MIST治疗后的常见副作用可能 与感染或血尿有关,有些病例在接受 这项治疗后一段时间内可能有尿潴留 症状。因此,某些患者或会在MIST 术后的一周到两周得使用尿导管。值 得一提的是,不同的MIST治疗法会 使用各自的方式保持排尿畅通,具体 的相关风险可咨询医生。
As for the recurrence rate of benign prostatic hyperplasia after treatment, there is currently no exact comparison of different treatments, but in some studies, the proportion of patients who had to undergo reoperation during the five-year period after receiving MIST ranged from 5 to 15%. Patients who underwent standard invasive procedures are believed to have lower rates of reoperation.