Ophthalmic innovation has made remarkable strides in recent years, with artificial intelligence (AI) playing a pivotal role in transforming patient care and clinical outcomes in the field of eye health.
AI's integration into ophthalmology has led to the development of advanced diagnostic tools, and personalized treatment plans. One of the most significant advancements is the use of AI algorithms for the early detection and management of retinal diseases, such as diabetic retinopathy, age-related macular degeneration, and glaucoma.
MedTech innovation in ophthalmology promises exciting advancements, such as AI-powered predictive analytics for personalized medicine, and the integration of virtual and augmented reality in ophthalmic training and patient education. These developments are not only making eye care more accessible and efficient but are also opening new avenues for treating complex ophthalmic conditions.Â
In National Healthcare Group Eye Institute, ophthalmic innovation and AI projects continue to advance eye care delivery. We work closely with our collaborators from Nanyang Technological University, Singapore Institute of Technology, and other industry partners such as DancingMind Pte. Ltd., Occutrack Medical Solutions Pte Ltd and many more to develop and trial new products and technology.  As ophthalmic innovation continues to evolve, the collaboration between engineers, clinicians, and researchers is vital to harnessing the full potential of AI, ensuring that technological advancements translate into tangible benefits for patients worldwide.
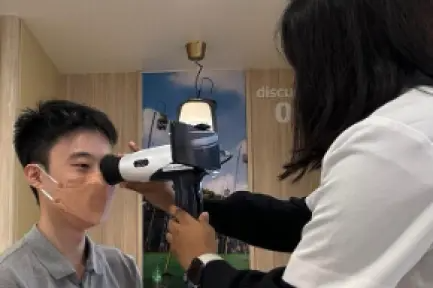
Automated cup-disc-ratio detection for early glaucoma detection: A pilot study using smartphone fundus images
To develop an automated vertical cup-to-disc ratio (vCDR) estimation system that can work across different types of retinal fundus images, including standard fundus images, ultra-widefield images and smartphone-based images.
3-D printed ocular model for cataract surgery training
A crucial step of cataract surgery involves the creation of a hole in the anterior capsule of the lens complex; this step is a termed “creating a continuous curvilinear capsulorrhexis (CCC)â€. Current methods of teaching this step of surgery involves using artificial eyes, porcine eyes, or simulators. However, these methods are either costly or suboptimal due to media opacity
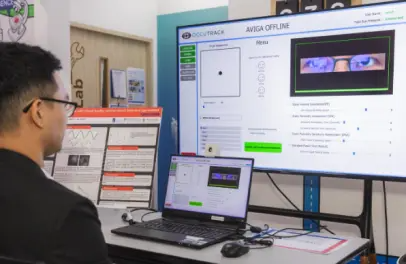
Automated Vision Assessment and Impairment Detection through Gaze Analysis ("AVIGA")
Wet Age-related Macular Degeneration (wAMD) occurs when abnormal blood vessels grow and leak deep within the macula, leading to scarring and irreversible vision loss.
Virtual Reality project for low vision rehabilitation
Visual field defects caused by stroke affect patients' activities of daily living and translate into difficulties with vision and orientation and mobility. Virtual reality (VR) has been shown to be beneficial for stroke rehabilitation, with its naturalistic environment facilitating learning from virtual to real-world application. The additional gamification element increases patients' motivation and compliance to therapy.
The aim of this research project is to evaluate the utility of VR gamification in the rehabilitation of patients with homonymous hemianopia. We hypothesise that the VR platform can achieve similar functional outcomes, if not better, compared to current existing methods (such as Dynavision).

